Department of Mechanical Engineering
Teaching Facilities |
|
|
| Engineering Building 1-1F |
K101 |
CAM Application Laboratory |
| K102 |
Machine Workshop |
K103
K104 |
Vehicle Dynamics Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 1-2F |
K201 |
Mechatronics Laboratory |
| K204 |
CAE Application Laboratory
(Computer-aided Mechanical Drawing Certification Examination Site)
(Computer-Assisted Stereoscopic
Drawing Certification Examination Site) |
| K205 |
Thermal Flow Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 1-4F |
K405 |
Automobile Chassis Practice Factory |
| K406 |
Automobile Engine Training Factory |
|
| Engineering Building 2-B1 |
J001 |
Vehicle Electrical Laboratory |
| J002 |
Vehicle Integrated Technology Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 2-1F |
J102 |
Creative Electromechanical Teaching Aids Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 2-2F |
J201 |
Single-Chip Microcomputer Laboratory (Single chip skills test site) |
| J203 |
Electronics Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 2-5F |
J501
J502 |
Precision Measurement Laboratory |
|
| Engineering Building 2-6F |
J601 |
Air Pressure Laboratory (Air Pressure Skill Certification Examination Room) |
| J602 |
Motor Laboratory |
|
| Outside the engineering
hall |
K105 |
Welding site |
| K107 |
Vehicle Maintenance Training Workshop |
|
| Cosmetics Building 1F |
B103 |
Motorcycle Training Factory |
| B103 |
Motorcycle Comprehensive Training Workshop |
|
Introduction to Mechanical Internship Factory |
| Practical Production Room Introduction |
| 1. |
This department was established to cooperate with the Ministry of
Education's key development characteristics of the vocational
education system and the cultivation of scientific and technological
education and precision manufacturing talents. The Practical
Production Room is one of the places where the department's students
take factory internship courses. It also supports the department's
teachers and students in teaching, research, experiments, etc., which
require equipment installation, parts or test piece production and
processing, as well as project services and other support work. |
| 2. |
This factory also provides equipment (machines, cutting tools, etc.)
for borrowing to assist students in special production courses and the
production and processing of simple parts that need to be processed
and assembled by themselves. This practical production studio is also
one of the training venues for mechanical processing and
manufacturing talents in the "Vehicle Parts Industry Professional
Talent Development Base", providing guidance and assistance to the
people participating in the training to acquire the professional skills
required in the workplace and to find employment smoothly after
completing the training. |
|
| Teaching objectives |
| 1. |
To cultivate students’ safe working habits and good working attitudes. |
| 2. |
Be familiar with the operation skills of various hand tools and the use
of precision measuring tools. |
| 3. |
Cultivate students’ ability to read drawings and plan processing and
manufacturing methods. |
| 4. |
Train students to be familiar with the knowledge related to machine
tool operation skills. |
| 5. |
Enable students to understand and solve process problems.
Location: Room K001, Basement of Engineering Building
|
|
| Instruments and Equipment |
| Instruments and Equipment |
Quantity |
| Hydraulic scraping table |
4 unit |
| Bench table |
6 unit |
| Drilling machine |
7 unit |
| Dust collecting grinder |
3 unit |
| Vertical sawing machine |
3 unit |
| Horizontal sawing machine |
1 unit |
| Lathe |
2 unit |
| Milling machine |
1 unit |
| Tool room |
1 unit |
|
OVERVIEW |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Introduction to CAM Application Laboratory |
| Laboratory Introduction |
| 1. |
This department was established to cooperate with the Ministry of Education's
key development characteristics of the vocational education system and the
cultivation of scientific and technological education and precision
manufacturing talents. The CAM Application Laboratory is designed to
enhance the department’s teaching and research capabilities in computer
aided manufacturing programs. At present, the construction of relevant
stamping die manufacturing technology has been completed. |
| 2. |
The main function of this laboratory is to provide a variety of computer-aided
mechanical manufacturing courses using CNC equipment and CAM related
software. Through course training, it cultivates high-end mechanical
manufacturing related talents for the industry. |
|
| Teaching objectives |
| 1. |
Be familiar with computer-aided manufacturing software and have the ability to
analyze engineering problems in the fields of material mechanics, vibration, heat
transfer, fluid mechanics, etc. |
| 2. |
Understand actual processing problems and use CAM software to establish
finished product models and manufacturing processes. |
| 3. |
Convert the results of computer simulation into CNC programs to process
various workpieces. |
|
| Instruments and Equipment |
| Instruments and Equipment |
Quantity |
| CNC machining center |
1 unit |
| CNC lathe |
1 unit |
| CNC machining center with 4th axis |
1 unit |
| CNC turning and milling machine |
1 unit |
| fine hole discharge machine |
1 unit |
| CNC Wire Cutting |
1 unit |
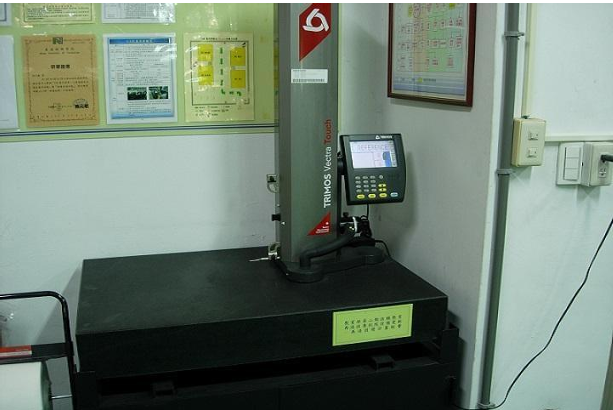
| Microcomputer electronic altimeter |
1 set |
|
OVERVIEW |
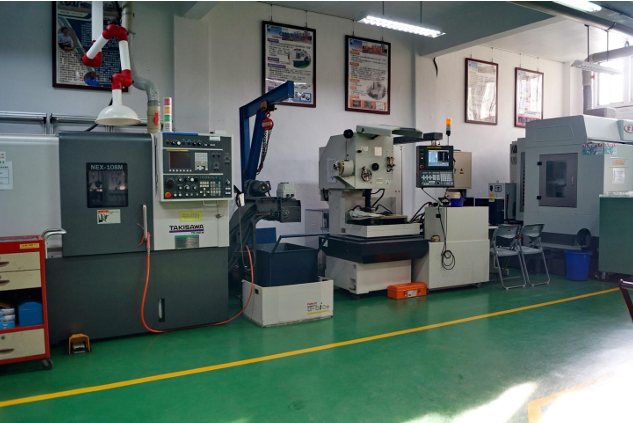
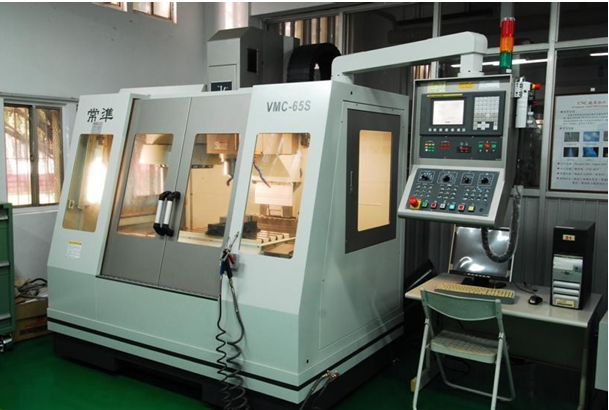
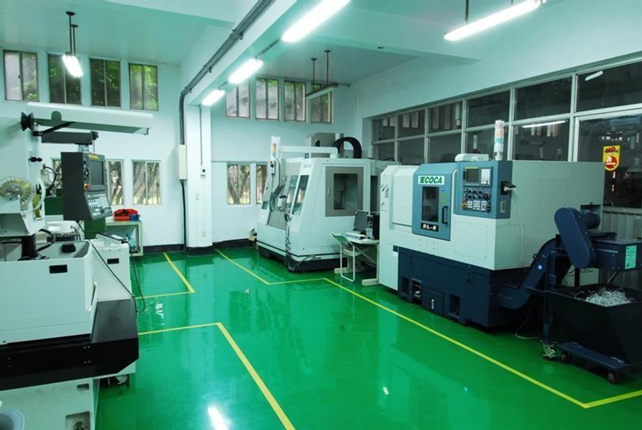 |
 |
CNC machining center |
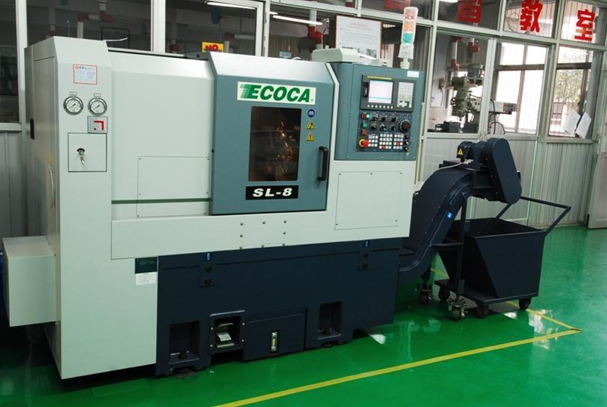
 |
CNC lathe |
 |
CNC Wire Cutting |
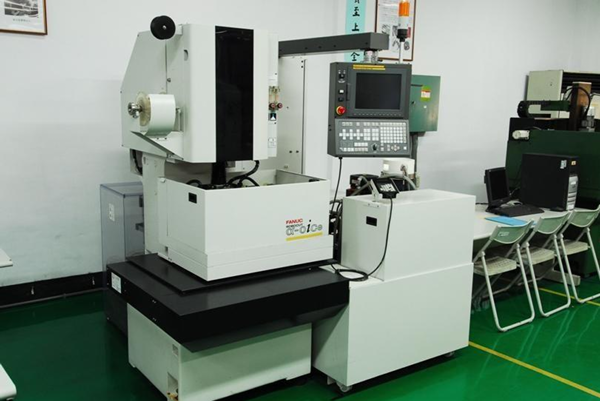 |
CNC machining center with 4th axis |
 |
CNC turning and milling machine |
 |
Fine hole discharge machine |
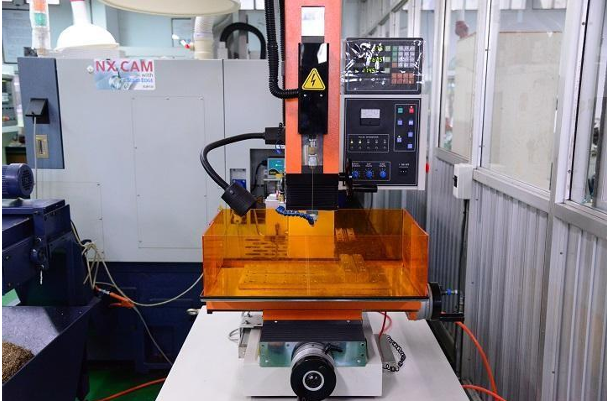 |
Microcomputer electronic altimeter |
 |
Mechanical Training Factory - Introduction to the Machine Room |
| The machine room is one of the places where the students of our department
take factory internship courses. It also supports the teaching, research,
experiments, etc. of teachers and students in the department, which require
equipment installation, parts or test piece production and processing, as well
as project services and other support work. It also provides equipment
(machines, cutting tools, etc.) for borrowing to assist students in special
production courses and the production and processing of simple parts for self
processing and assembly. This machine room is also one of the training sites
for mechanical processing and manufacturing talents in the "Vehicle Parts
Industry Professional Talent Development Base", providing guidance and
assistance to the people participating in the training so that they can acquire
the professional skills required in the workplace and find employment
smoothly after completing the training. |
| objectives |
| 1. |
Cultivate students’ safe working habits and good working attitudes. |
| 2. |
Be familiar with the operation skills of various hand tools and the use of
precision measuring tools. |
| 3. |
Cultivate students’ ability to read drawings and plan processing and
manufacturing methods. |
| 4. |
Train students to be familiar with the knowledge related to machine tool
operation skills. |
| 5. |
To enable students to understand and solve process problems |
|
| Instruments and Equipment |
| Device Space Name |
Quantity |
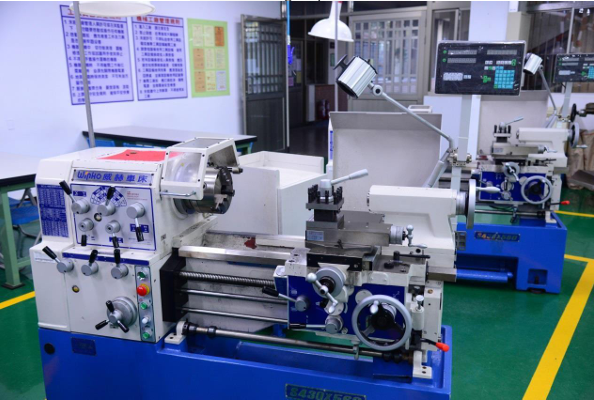
| Precision high speed lathes |
16 units |
| Precision milling machines |
3 units |
| Surface grinder |
1 unit |
| Dust collecting grinder |
1 unit |
| Drilling machine |
1 unit |
| Vacuum equipment |
1 s |
|
Overview |
 |
 |
Precision high speed lathes |
 |
Precision milling machines |
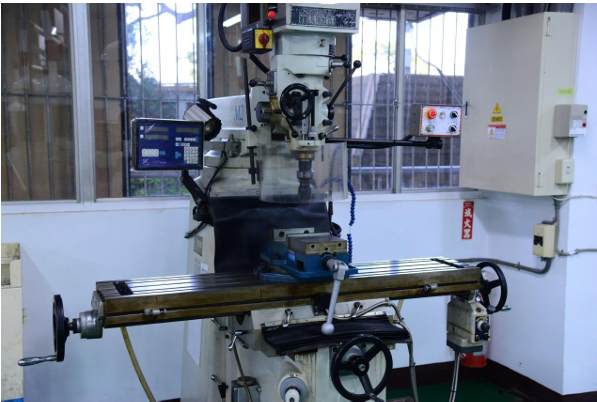 |
Surface grinder |
 |
Dust collecting grinder Dust collecting grinder |
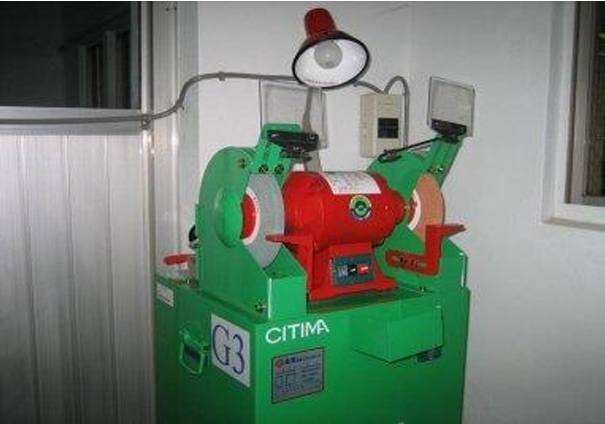 |
Drilling machine |
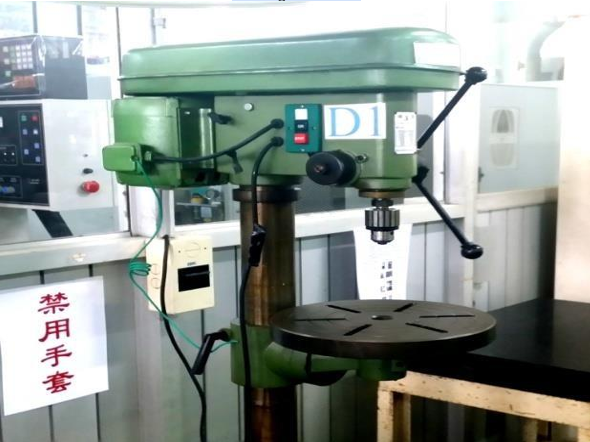 |
Vacuum equipment |
 |
Introduction to the Mechatronics Integration Laboratory |
| Laboratory Overview |
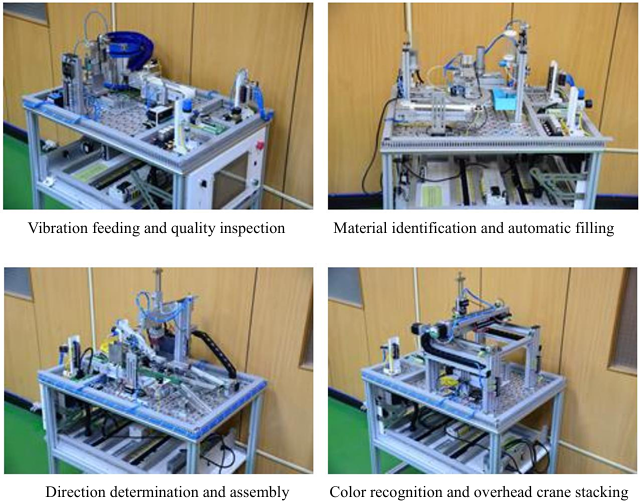
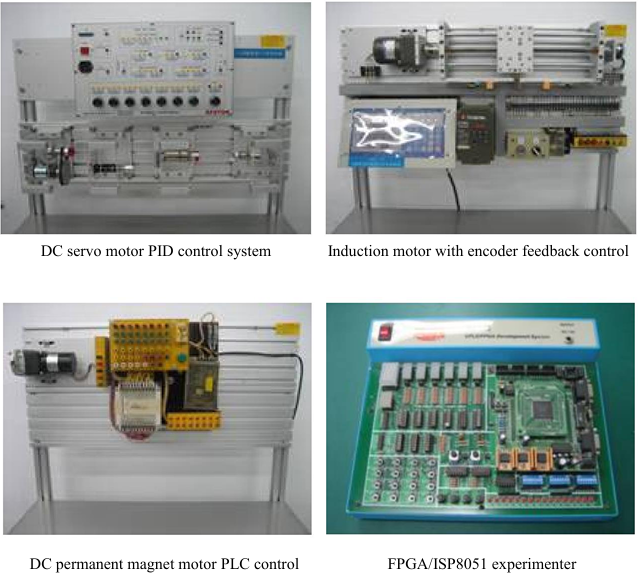
| This laboratory is an elective course for junior and senior students in the department, aimed at cultivating talent in the field of mechatronics integration. The main equipment includes: |
| • |
Vibration feeding and quality inspection |
| • |
Material identification and automatic filling |
| • |
Direction determination and assembly |
| • |
Color recognition and overhead crane stacking |
| • |
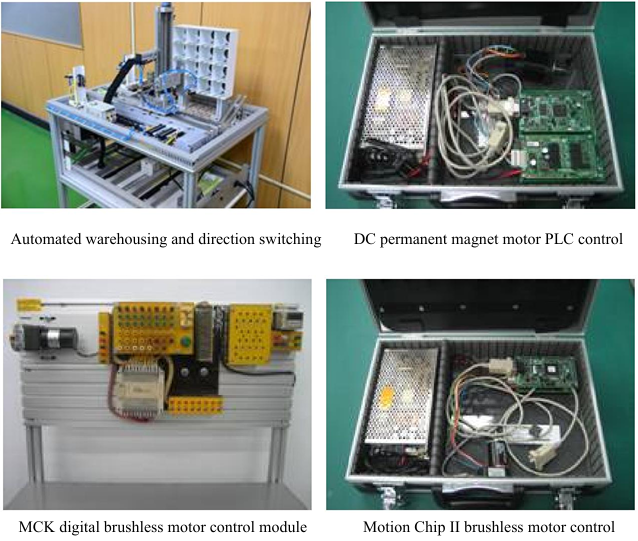
Automated warehousing and direction switching |
| • |
Shape recognition and conveyor inspection station |
| • |
Color recognition and posture adjustment inspection station |
| • |
Posture determination and switching inspection station |
| • |
Material sorting and processing inspection station |
| • |
Hydraulic punching and forming inspection station |
| • |
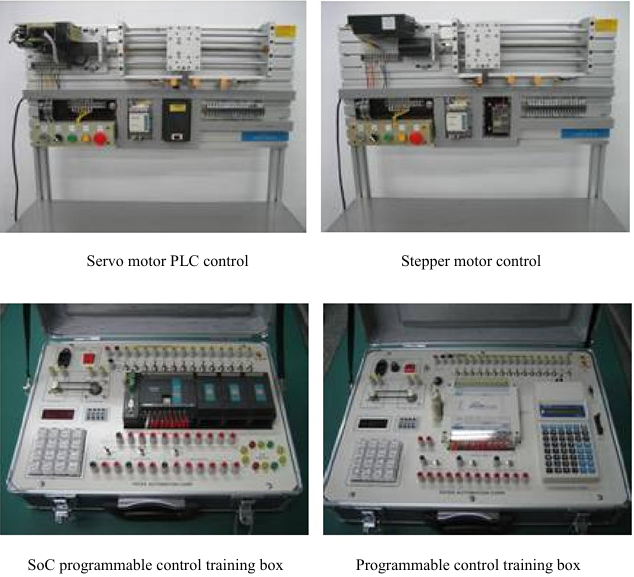
Programmable control training boxes |
| • |
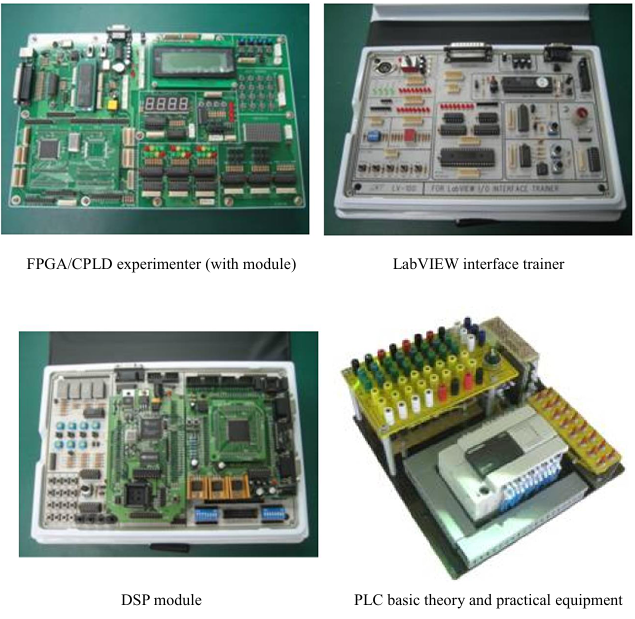
LabVIEW interface trainers |
| • |
FPGA/CPLD experimenters (with modules) |
| • |
Silent air compressors and air tanks |
| • |
FPGA/ISP8051 experimenters |
| • |
Psoc System-on-Chip experimenters |
| • |
DSP modules |
| • |
Programmable motor control application platforms |
| • |
Motion Chip II |
| • |
MCK digital brushless motor control teaching modules |
|
| Teaching objectives |
| 1. |
This laboratory mainly focuses on mechatronics integration, motor control, and logic design.
The goal is to introduce a variety of control systems such as servo systems, motor control system
applications, and PLC applications. |
| 2. |
The lab was established to align with the program curriculum, utilizing existing equipment to
train senior students in preparation for the national Class C Mechatronics Technician
Certification. It aims to cultivate students with both practical and research capabilities. |
| 3. |
The lab supports courses such as "Automation Practice", "PLC Programmable Control",
"Pneumatic Control and Experimentation", "Hydraulic and Pneumatic Practice", and
"Mechatronics Integration". It uses the available equipment to prepare students for the national
Class C Mechatronics Certification, fostering a blend of hands-on skills and academic research
ability. |
|
Laboratory Location
Room K201, 2nd Floor, Engineering Building I. |
Supervising Professor
Chih-Yi Chang |
Full Laboratory View |
 |
Equipment List |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Lab Projects |
| 1. |
PLC motor control practice |
| 2. |
PLC training box simulation practice |
| 3. |
Mechatronics automation application |
| 4. |
Servo motor control practice |
| 5. |
Logic design practice |
| 6. |
LabVIEW graphical control practice |
|
Introduction to the CAE Applications Laboratory |
| Laboratory Overview |
| In recent years, with the rapid advancement of computer technology, the demand for
professionals skilled in computer-aided design, manufacturing, and analysis has become urgent,
particularly as traditional industries face the need for upgrades and full-scale digitalization. Taiwan,
in particular, is transitioning from a manufacturing-based industry to one focused on research and
design. Accelerating product development through computer technology has become an essential task
across all industries. |
| This laboratory is primarily intended to support computer-aided engineering (CAE) and
computer-aided design (CAD) coursework. Through these courses, the lab helps cultivate product
development talent for industry. |
| The lab is also an official testing site for the Class B and C certification exams in "Computer
Aided Mechanical Design and Drafting" and Class C in "Computer-Aided 3D Drafting." It is fully
equipped with the latest software and hardware to meet certification requirements and offers
preparatory courses to assist students in obtaining certifications. The number of successful candidates
continues to increase each year. |
| Teaching Objectives |
| 1. |
Gain proficiency in computer-aided engineering analysis software and develop the ability to
analyze engineering problems in areas such as mechanics of materials, vibration, heat transfer,
and fluid mechanics. |
| 2. |
Understand practical engineering problems and use software to build analytical models and
workflows. |
| 3. |
Use computer simulations to verify theoretical knowledge learned in various disciplines. |
|
| Laboratory Location |
| Room K204, 2nd Floor, Engineering Building I. |
| Supervising Professor |
| Professor Chih-Yi Chang |
| Equipment List |
| Equipment Name |
Quantity |
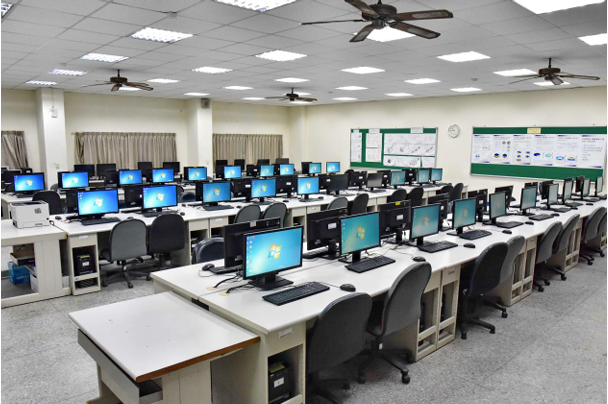
| Intel Core i7-10700 desktop PC (22" LCD monitor, 32GB RAM, 512GB
SSD, 1TB HDD, NVIDIA Quadro P1000 graphics card, system restore
card) |
51units |
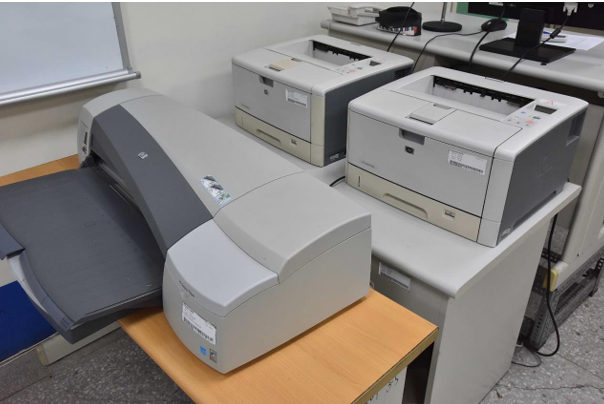
| A3 Network Laser Printer (HP LaserJet M42625dn) |
1 units |
| A3 Network Laser Printer (HP LaserJet 5200L) |
1 unit |
| A2 Network Inkjet Plotter (HP Designjet 110 plus) |
1 unit |
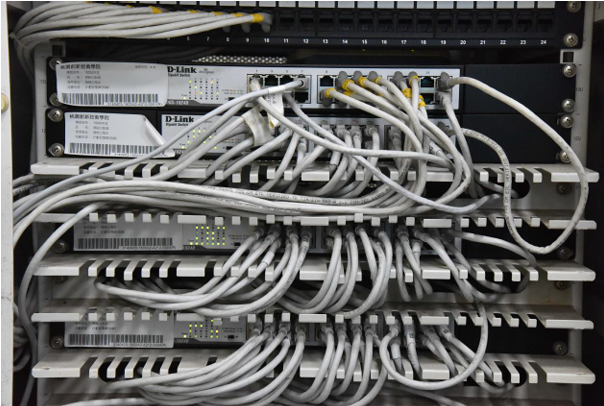
| Network Cabling (including rack and switch) |
1 set |
| Monitoring System Software (Broadcast Teaching) Monitoring System
1 set
Software (Broadcast Teaching) |
1 set |
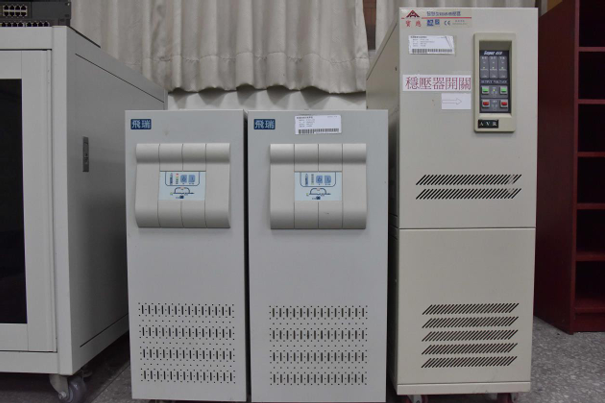
| UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply + Voltage Regulator (25KW) |
1 set |
|
Equipment List |
 |
 |
A2 inkjet plotter and A3 laser printer
|
 |
UPS and voltage regulator |
 |
Switch-type network hub
|
 |
| Software & Courses Offered |
| No. |
Software |
Licenses |
Related Courses |
| 1 |
Inventor Professional 2021 |
100users |
Computer-Aided Drawing (required)
Inventor 3D Drawing (elective)
3D CAD (elective)
Mechanical CAD (elective)
Class C and B exam prep courses |
| 2 |
AutoCAD 2021 |
100users |
Mechanical Drawing (required) |
| 3 |
COMSOL Multiphysics 3.5a |
60users |
Computer-Aided Engineering Analysis (elective) |
| 4 |
SolidWorks 2019 |
60users |
Computer-Aided Drawing (required)
SolidWorks 3D Drawing (elective)
Advanced Drawing (elective) |
| 5 |
CATIA V5R21 (Education Edition) |
20users |
CATIA 3D Drawing (elective) |
| 6 |
MasterCAM 2020 (Education Edition) |
60users |
Programming and Cutting Tools (elective) |
| 7 |
MATLAB 7.0 |
100users |
Numerical Analysis (elective)
Engineering Applications of MATLAB (elective) |
| 8 |
CyberLink PowerDirector 18 |
60users |
Digital Video Editing (elective) |
|
Introduction to the Thermo-Fluid Laboratory |
| Laboratory Overview |
The purpose of this laboratory is to train beginners in thermo-fluid experimental techniques and to
inspire research-oriented thinking in students, enabling them to validate theory through practical
experimentation. The goal is to help students gain a more accurate, in-depth, and concrete
understanding of thermal-fluid sciences.
This laboratory is particularly focused on providing students with experimental knowledge and skills
in thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, fluid machinery, and green energy. In addition to experiments
related to thermal and fluid systems, green energy systems such as fuel cells, solar power, and wind
power are also included, making the experiments both practical and comprehensive.
The lab is suitable for a semester-long course (2–3 hours per session), and the experiments are divided
into three major categories: |
| 1. Thermal Experiments: |
| • |
Heat exchanger test |
| • |
Heat conduction experiment |
| • |
Fire point test |
| • |
ASTM distillation test |
| • |
Viscosity test |
| • |
Calorific value measurement |
|
| 2. Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Machinery Experiments: |
| • |
Flow meter test |
| • |
Pump performance test |
| • |
Venturi tube experiment |
| • |
Pipeline friction loss test |
| • |
Wind tunnel test |
|
| 3. Green Energy Experiments: |
| • |
Fuel cell test |
| • |
Wind energy training system |
| • |
Solar energy experiment |
|
| Teaching Objectives |
| 1. |
To cultivate students' skills in thermal, energy, fluid mechanics, and fluid machinery experiments,
and to inspire research-based thinking by connecting theory and practice. Students will gain a
solid foundation in thermodynamics, heat transfer, and fluid mechanics through this integration. |
| 2. |
Each experiment is designed to be comprehensive yet easy to understand. The course proceeds in
a step-by-step manner, beginning with the objective and theoretical background, followed by
detailed steps and designed data sheets. This ensures students can accurately observe, record, and
analyze experimental results, and reflect on the findings to develop structured and practical
knowledge. |
| 3. |
Students are expected not only to understand the experimental principles and procedures but also
to analyze the discrepancies between data and theory and identify possible sources of error. |
|
| Laboratory Location |
| Room K205, 2nd Floor, Engineering Building I. |
| Supervising Professor |
| Professor Chih-Yi Chang |
| Laboratory Equipment |
| Thermal Experiment Equipment |
| No. |
Equipment Name |
Devices Used |
| 1 |
Heat Exchanger Experiment |
HEX-300E Water-to-water exchanger, thermometer,
flow meter |
| 2 |
Heat Conduction Measurement |
ET100 apparatus, temperature controller, timer, digital
thermometer |
| 3 |
Calorific Value Measurement |
PARR 1341 Calorimeter, high-pressure oxygen tank,
precision balance, ignition device |
| 4 |
Fire Point Test |
Closed flash point tester, gas cylinder, thermometer,
kerosene, diesel |
| 5 |
ASTM Distillation Test |
Wind shield, cooling bath, condenser tube, distillation
flask, thermometer, measuring cylinder, unleaded
gasoline |
| 6 |
Viscosity Test |
Saybolt viscometer, rotational viscometer |
|
| Fluid Mechanics Equipment |
| No. |
Equipment Name |
Devices Used |
| 1 |
Venturi Tube Test |
TQ-H5 Venturi setup, hydraulic bench |
| 2 |
Flow Measurement Test |
TQ-H10 Flow meter, hydraulic bench |
| 3 |
Pipeline Head Loss Test |
TQ-H34 Loss experiment setup, hydraulic bench |
| 4 |
Pump Performance Test |
TQ-H32 Pump test setup (parallel/series), hydraulic
bench |
| 5 |
Valve Characteristics Test |
Valve test bench, coupler |
| 6 |
Reynolds Number Experiment |
Glass tubes, heating unit, Reynolds apparatus |
| 7 |
Wind Tunnel Test |
Wind tunnel, motor, data acquisition system |
|
| Green Energy Experiment Equipment |
| No. |
Equipment Name |
Devices Used |
| 1 |
Fuel Cell System Test |
Solar module, electrolyzer, fuel cell, load module,
measurement module, analysis software |
| 2 |
Solar Power Module |
IKS solar training platform, solar panels, shading
panels, multimeters, sensors, radiation simulators,
batteries, loads |
| 3 |
Wind Power Module |
IKS wind training platform, wind box, anemometer,
multimeters, axial turbine components, blades,
batteries, loads |
|
Lab Overview Photos |
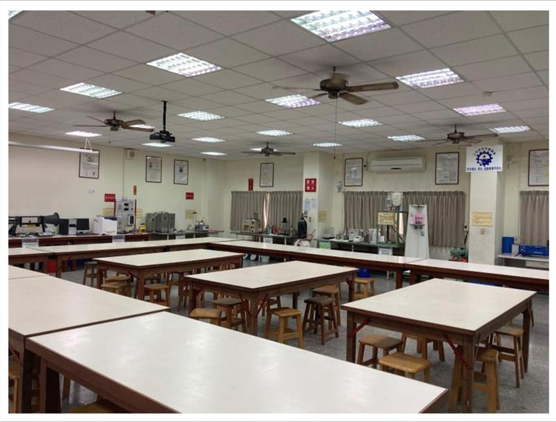 |
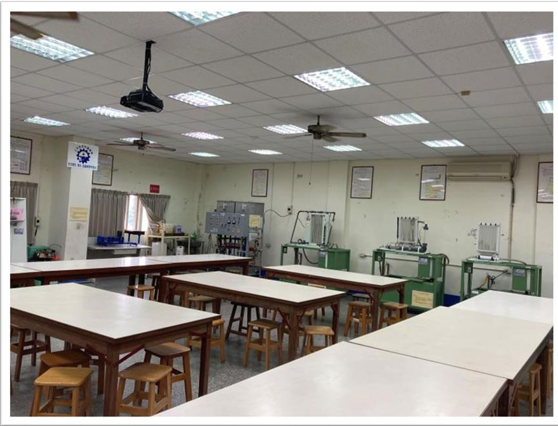 |
 |
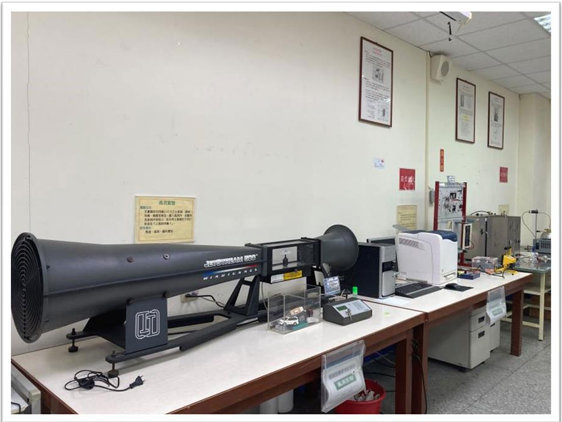 |
| Main Equipment and Experiment Objectives |
| Thermal Experiment Equipment |
| No. |
Experiment Objectives |
| 1 |
Heat Exchanger Experiment
Different flow configurations are used to
allow fluids at different temperatures to
flow through a double-pipe heat
exchanger. Students measure the heat
transfer rate, thermal conductivity, and
temperature distribution, and compare
heat transfer efficiency across conditions. |
 |
| 2 |
Heat Conductivity Measurement
Using a thermal conductivity apparatus,
students measure the thermal conductivity
coefficients of various materials. |
 |
| 3 |
Calorific Value Measurement
Calorific value refers to the heat released
from burning 1 gram of fuel. Typically
measured using a calorimeter, this
experiment employs an adiabatic
calorimeter to determine the calorific
value of solid or liquid fuels. |
 |
| 4 |
Fire Point Test
A closed cup flash point tester is used to
measure the flash points of various fuels
and lubricants. Students also learn the
correct operation of testing instruments
and understand fuel volatility and flash
points. |
 |
| 5 |
ASTM Distillation Test
Using ASTM standard distillation
equipment, this experiment obtains the
evaporation curve of engine fuel to
evaluate its purity and volatility, serving
as a reference for fuel quality control. |
 |
| 6 |
Viscosity Test
• The Saybolt viscometer measures the
time required for oil to flow through a
standard orifice at a set temperature,
indicating viscosity.
• A rotational viscometer is also used to
measure viscosity, allowing
comparison and validation of results
obtained from both instruments. |
 |
|
| Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machinery Equipment |
| No. |
Experiment Objectives |
| 1 |
Venturi Meter Test
Tests the relationship between velocity
and pressure at various sections of a
Venturi tube and calculates the flow
coefficient by comparing theoretical and
actual flow rates. |
 |
| 2 |
Flow Measurement Test
Introduces the principles and usage of
various flow meters including Venturi
meters, orifice plates, and rotameters.
Students explore the relationship between
flow coefficients and Reynolds numbers. |
 |
| 3 |
Head Loss Test of Pipeline
Investigates energy losses caused by fluid
viscosity, pipe wall roughness, and
velocity changes as water flows through
pipelines and fittings. Helps students
understand key design considerations in
piping systems. |
 |
| 4 |
Pump Performance Test
Measures flow rate, total head, and
efficiency of centrifugal pumps at
different speeds. Students create
performance curves and examine how
series or parallel pump configurations
affect performance. |
 |
| 5 |
Valve Characteristic Test
Measures pressure drop across five types
of valves—check, gate, ball, plug, and
angle—under different flow rates to
determine geometric loss coefficients for
design and application reference. |
 |
| 6 |
Reynolds Number Experiment
Measures flow rate in a circular pipe and
uses dye to visualize the differences
between laminar and turbulent flows.
Helps students understand and determine
the critical Reynolds number for flow
transition. |
 |
| 7 |
Wind Tunnel Test
Small-scale models (e.g., trains, cars,
aircraft, wings) are placed in a wind
tunnel to measure flow velocity and drag
force. Students calculate drag coefficients
(Cd) for real objects under various speeds. |
 |
|
| Green Energy Equipment |
| No. |
Experiment Objectives |
| 1 |
Fuel Cell System Test
This experiment explores the process of using
solar panels to power an electrolyzer that
produces hydrogen and oxygen. These gases are
then used in a fuel cell, which generates
electricity through electrochemical reactions to
power loads like bulbs, motors, or model cars.
Students determine the electrolyzer’s
performance curve, efficiency, and analyze the
series/parallel configuration effects on the fuel
cell system. |
 |
| 2 |
Solar Power Module
Solar cells convert sunlight directly into
electricity using the photoelectric effect.
Students use the IKS solar training platform to
assemble modules and conduct experiments
including:
•Open-circuit voltage and short-circuit
current under various shading
conditions
• Series and parallel configurations
• I-V characteristics under different
illumination levels
•Maximum power point and efficiency
evaluations |
 |
| 3 |
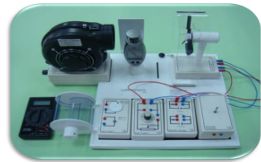
Wind Power Module
This module converts wind energy into
mechanical energy by rotating wind turbine
blades. A speed increaser boosts the rotation
rate to drive a generator. The generated AC
voltage is then regulated and converted into DC
power stored in batteries. |
 |
|
Vehicle Electrical Laboratory |
| Introduction: |
| This laboratory is the venue for the vehicle engineering internship courses
(II III IV V) for the vehicle engineering group students of our department. It
also supports the teaching, research, and experiments of teachers and students in
the department, as well as the construction and education cooperation project
services. |
| Objectives: |
| Establish students' understanding of advanced vehicle electronic motor control
applications in various vehicle systems including vehicle sensing control, CAN
network |
| The technology of road control, hybrid electric vehicle control, body circuit, air
conditioning, steering positioning, etc. has theoretical concept verification |
| The training provides students with practical experience in diagnosis and
maintenance, so as to train them to become maintenance engineers of advanced
vehicles, or to become research engineers. |
| Design engineer. The work of this laboratory is mainly devoted to the following four
points: |
| 1. |
Planning and implementation of vehicle maintenance education, training,
certification and competition. |
| 2. |
Research, develop and produce vehicle engineering education and training
equipment, handouts and manuals. |
| 3. |
Provide technical support and experience consultation for advanced diagnostics of
various vehicle systems. |
| 4. |
Vehicle system components, performance testing and analysis.
Overview |
|
| Overview |
 |
| Instruments and Equipment |
| The automotive electrical system laboratory is equipped with vehicle sensing and
control demonstration platform, CAN bus control demonstration platform, hybrid
electric vehicle, computer-controlled engine demonstration platform, body circuit
demonstration platform, central locking demonstration platform, automobile air
conditioning demonstration platform, automatic constant temperature air
conditioning demonstration platform, various test analysis and diagnostic
instruments, 4WS four-wheel steering training vehicle, and four-wheel alignment
detection equipment. |
 |
Creative M&E Teaching Aids Laboratory |
| Laboratory Profile: |
| The "Creative Electromechanical Teaching Aids Laboratory", which attaches equal importance
to teaching and research, practice and production, is also the listing office and one of the main R&D
bases of the "Electromechanical Power System and Micro Molding Technology R&D Center" of the
Department. In addition to teaching and R&D, the laboratory has three functions: |
| 1. |
For the special finished product display and display of electromechanical power and 3D
printing of the department. |
| 2. |
For the production and venue of the Department's practical topics and the construction of
competition simulation venues. |
| 3. |
It is a research room for teachers, students and graduate students of the Department's special
research and development projects |
|
| In short, this laboratory is a multi-functional purpose, which can be used for practical
production courses in mechatronics and 3D printing, and when necessary, it can be used as a
production and maintenance base for external competitions and a display venue for thematic
finished products. |
| Teaching Objectives: |
| Creativity is not limited to men and women, young and old, and school experience, you can get
good creative ideas at any time around your life, and then put practical ideas into concrete practice,
which can become inventions. Good ideas must be commercialized to be shared by human beings,
and the process of commercialization must be realized by mechatronics engineering and 3D printing
technology |
| 1. |
Familiarity with the laws of creativity; |
| 2. |
cultivating creative crafts; |
| 3. |
Combined with 3D printing skills: |
| 4. |
Applied Mechatronics Engineering Techniques: |
| 5. |
Produce creative 3D printing works combined with mechatronics. |
|
| A full view of the laboratory |
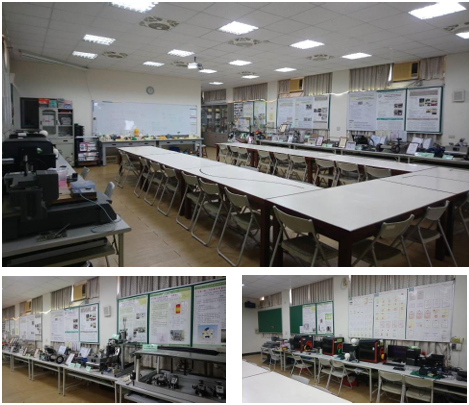 |
| Instruments and equipment |
| In terms of instruments and equipment, the laboratory has 3D printers, CNC engraving and
milling machines, digital oscilloscopes, high-speed CCD cameras, and various single-chip
simulationsIn addition to the research equipment such as burners, there are also professional sheet
metal processing areas, circuit board production areas, electronic circuit welding testing areas and
parts and material warehouses, supplemented by the latest mechanical and electronic drawing and
wiring software, so that the center can design, produce and assemble one-stop research and
development tools, environment and capabilities, so whether it is teaching or research, it can fully
meet the needs of teachers and students of the department. |
 |
Single-chip microcomputer laboratory |
| Laboratory Profile: |
| A single chip is a single chip that integrates the CPU, memory, and I/O ports of a computer
into a single IC chip, and its function is quite small and small. Because the single-chip structure is
simpler than the general-purpose microcomputer, the price is lower and the development is easier,
so it is used in industrial control and home appliances, also known as microcontrollers. The
laboratory aims at the principle and application of a single-chip microcomputer, using Arduino and
Raspberry Pi as the control platform, using IDE and Python The compiler is used as a programming
tool, combined with various sensor components, so that students can learn the use of sensor
hardware from a single-chip microcomputer to strengthen software programming skills, and
combined with 3D printing technology, to cultivate students' ability to produce special topics. |
| Teaching Objectives: |
| 1. |
To enable students to understand the structure and principles of a single-chip microcomputer
and the syntax of its programs. |
| 2. |
The internship explores the different application circuits and programming skills of a single
chip. |
| 3. |
Tutor students to obtain a single-chip C certificate or above to enhance students'
competitiveness. |
|
| A full view of the laboratory |
 |
| Instruments and equipment |
| In terms of instruments and equipment, the laboratory has 32 personal computers, digital
oscilloscopes, signal generators, power supplies, heat guns, Arduino control boards, Raspberry Pi
control boards, and single-chip microcomputer simulationsIn addition to the research equipment
such as burners, there are also professional processing areas, circuit board production areas,
electronic circuit welding testing areas and parts and material warehouses, supplemented by the
latest mechanical and electronic drawing wiring and circuit board design software, so that the
laboratory can fully meet the needs of teachers and students in the department from design,
production to assembly of research and development tools, environment and capabilities. |
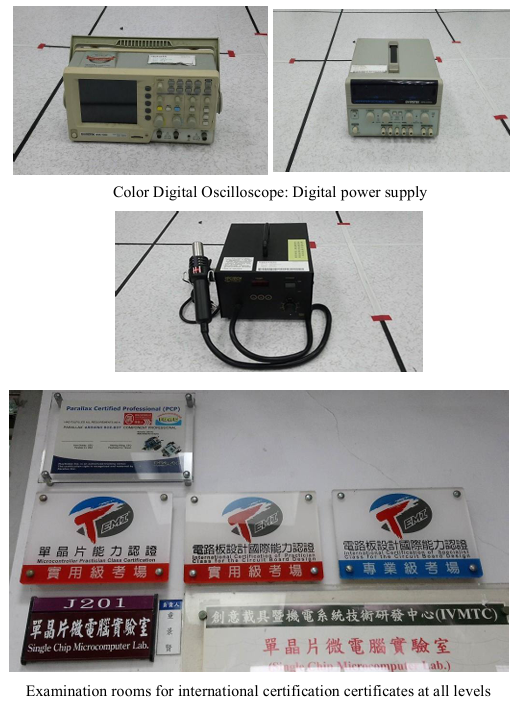 |
| Research Results |
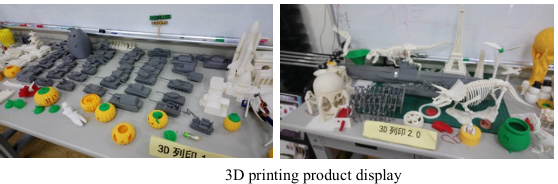 |
Electronics laboratory |
| This laboratory aims to cultivate students' understanding of electronic
components , familiarity with instrument operation, establishment of electronic
circuits, confidence in independent work, and comparison of electronic principles and
experiments , so that theory and practice can be mutually confirmed, and used to
inspire research and thinking, as well as the ability to troubleshoot, to gain a clearer,
deeper and more specific understanding of practice. |
| laboratory equipment: |
 |
| Electronic circuit experiment: compulsory course for the daytime department and
compulsory course for the continuing education department of the Department of
Mechanical Engineering |
 |
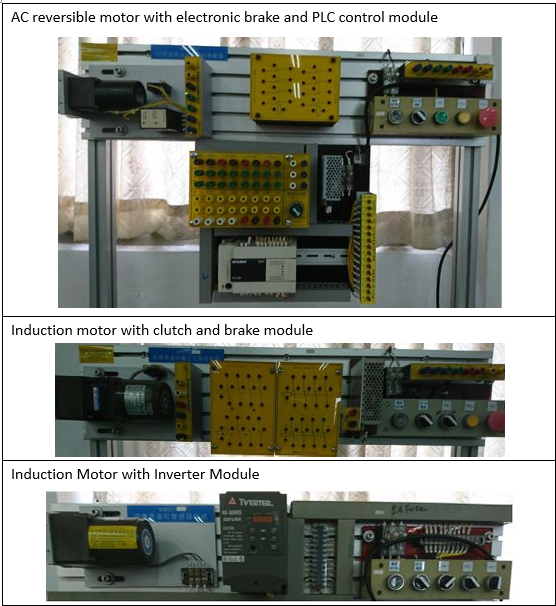
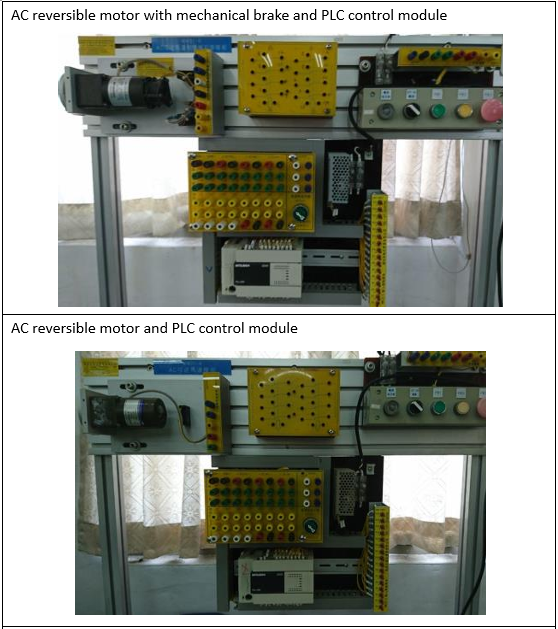
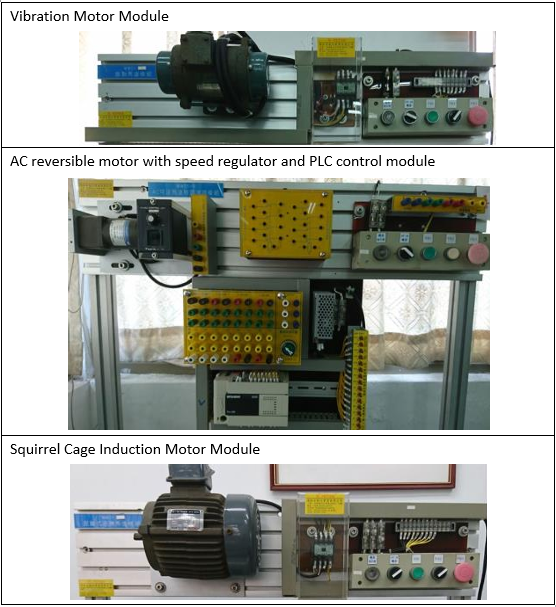
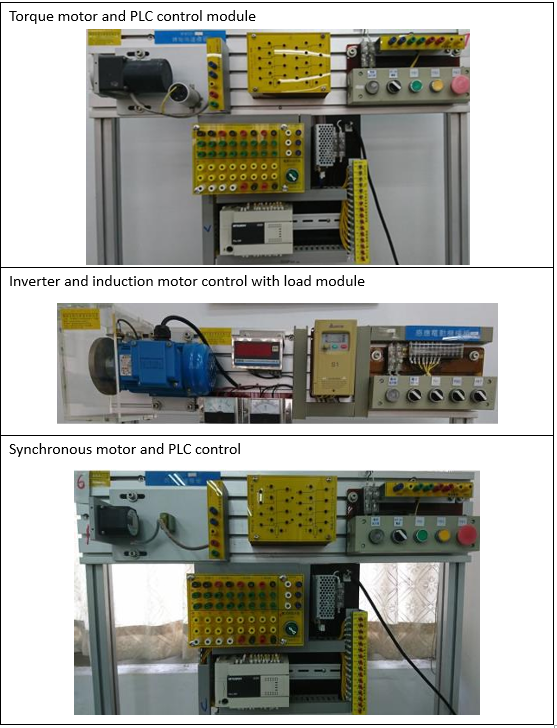
Electrical Machinery Laboratory |
| This teaching laboratory provides space and equipment suitable for general
industrial motors and generators, PLC control, and wiring practice. Through course
training and hands-on practice, students are cultivated to have the ability to design
PLC and integrate peripheral systems, verify the theoretical knowledge learned in the
classroom, and enhance practical ability and experience. Cultivate electromechanical
practical control talents for the industry. |
| Teaching objectives: |
| 1. |
Let students understand the functions, uses, structures, specifications, etc. of
various motors. |
| 2. |
Cultivate students with various motor and PLC control and wiring skills
EquipmentS: |
|
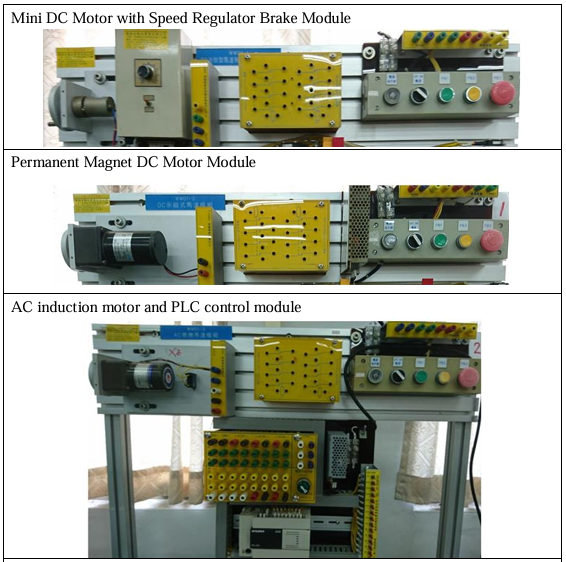 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
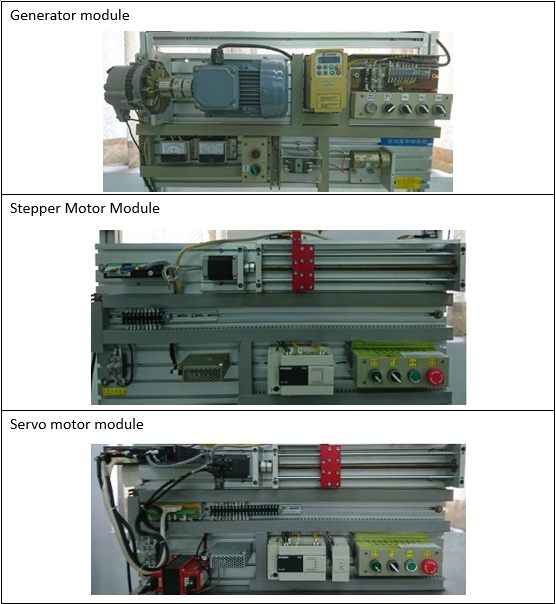 |
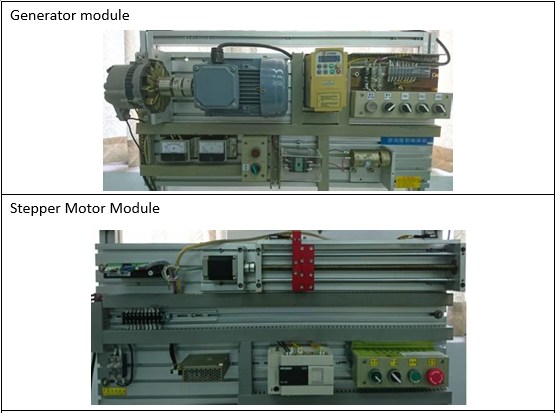 |
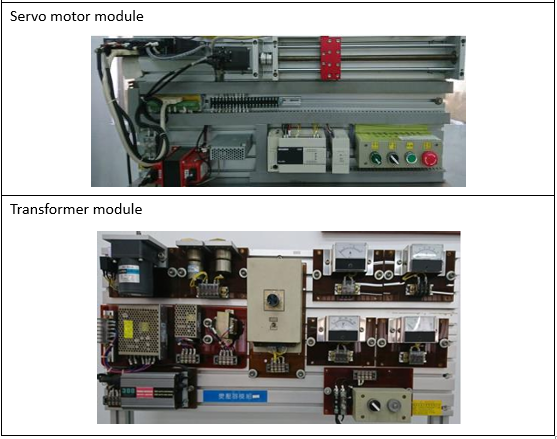 |
| Classroom |
 |
Introduction to the locomotive practice factory, and introduction to the laboratory |
| With the rise of computer technology in recent years, traditional carburetor motorcycles are
facing elimination, and the era of full computerization has arrived. The demand for computer
diagnosis and repair and signal analysis and diagnosis talents is very urgent, especially in Taiwan,
which is a country with a high density of motorcycles (speed cars). The technology of using
computers for diagnosis involves basic principles such as basic electricity, electronics, and electrical
engineering. The main function of this laboratory is to use computer diagnostic equipment to
provide all the basic concept courses required for computer diagnosis. Through the training of
diagnostic courses, it provides the motorcycle repair industry with the talents needed in the future.
The laboratory is also the training location for the "Motorcycle Repair" Level B and C courses. It is
equipped with the latest diagnostic equipment and fully meets the requirements of candidates. It
guides students to obtain the Motorcycle Repair Level B and C certificates and helps students
successfully obtain the certificates |
| Teaching objectives: |
| 1. |
To enable students to understand the skills and knowledge of the following internship projects:
such as locomotive electrical system starting, charging, lighting, signaling, etc.
Component identification, resistance measurement, circuit measurement and repair,
troubleshooting, etc. |
| 2. |
To familiarize students with the control functions of various components through diagnostic
testing. |
| 3. |
Cultivate students’ proper professional ethics and work attitudeTeaching objectives |
|
| Instruments and Equipment |
| Device Space Name |
Quantity |
| dengen/HR-MAX70D/1 Full-wave rectifier
fast charger |
1 |
| QROTECH/QRO-201 Two-Gas Exhaust
Analyzer |
1 |
| EMOTO/ED-100 Diagnostic Instrument |
1 |
| Jet engine fuel pressure gauge |
2 |
| DET-610 Tachometer |
3 groups |
| Nine-in-one motorcycle diagnostic instrument |
2 sets |
| Four-stroke jet locomotive engine anatomical
model |
1 Group |
|
| Laboratory Overview : |
 |
 |
| subject |
Course Title |
class |
Course Overview |
| 1 |
Locomotive inspection
practice |
Grade 3 of the
fifth-year
college Grade
4 of the fifth
year college |
Motorcycle repair and maintenance
Class B tutoring Motorcycle jet
engine repair Electronic jet sensor
principle and detection
|
| 2 |
Locomotive Principles
and Practice |
Grade 1 |
Motorcycle repair and
maintenance level C tutoring
Motorcycle component
disassembly and assembly
Motorcycle component
measurement |
|
Introduction to Automobile Engine Internship Factory |
| Laboratory introduction |
| In recent years, with the rise of computer technology, traditional old-fashioned cars are facing
elimination, and the era of comprehensive new technology has arrived. |
| 1. |
.The demand for talents in brain diagnosis, repair and signal analysis is very urgent,
especially as Taiwan is a country with a high density of automobiles Brain-based diagnosis
technology involves basic principles such as basic electricity, electronics, and introduction
to electrical engineering, and the main function of this laboratory is |
| 2. |
.It is a course that uses computer diagnostic equipment and all the basic concepts
required for diagnosis of various instruments. Through the training of diagnostic courses,
it provides |
| 3. |
The auto repair industry provides the talent needed for the future. This laboratory is also
a training venue for the Level C course of "Car Maintenance", equipped with
The new diagnostic equipment fully meets the requirements of candidates. It helps
students obtain the Class C automobile maintenance certificate and helps them
successfully pass the examination. Obtain the certificate. |
|
| Teaching objectives: |
| 1. |
Let students understand the skills and knowledge of the following internship projects: such as
identification of components such as starting, charging, lighting, and signals in the automotive
electrical system.
Resistance measurement, circuit measurement and repair, component disassembly and assembly,
full vehicle maintenance, etc |
| 2. |
Make students familiar with the functions, structures and disassembly and assembly skills of
each component. |
| 3. |
Cultivate students’ proper professional ethics and work attitude.
Laboratory location |
|
| Instructor Lin Dequan |
| Equipment |
Quan. |
| Ultra-thin flat-type jacking |
2 units |
| Four wheel jack |
1 set |
| Tool cart set |
1 set |
| Injection engine fuel pressure gauge |
1 set |
| Current hook meter |
1 set |
| Cylinder compression pressure gauge |
1 set |
| Water tank pressure gauge |
1 set |
| Car computer diagnostic tool V70 |
1 unit |
|
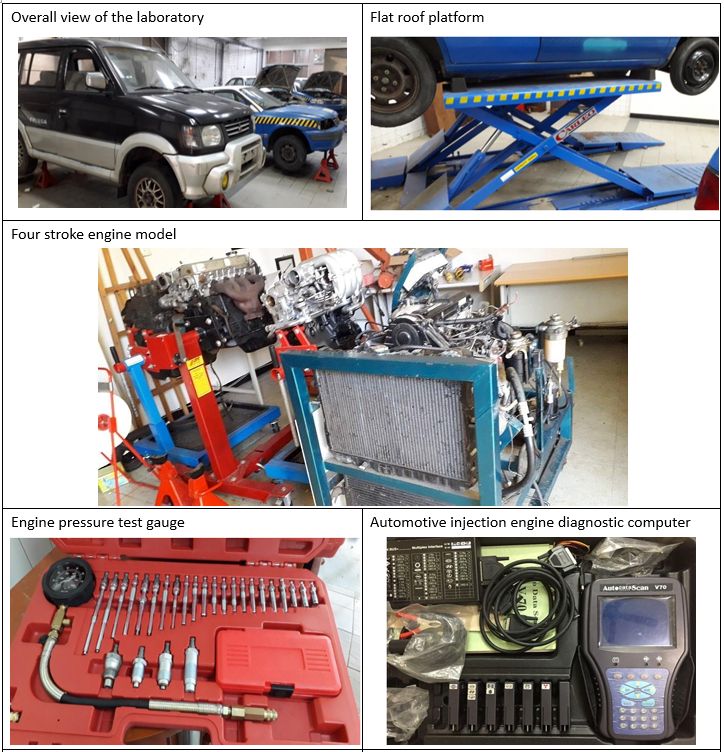 |
| Offer courses |
| subject |
Course Name |
Class |
Course Overview |
| 1 |
Automobile
Maintenance Internship
(V) |
Comprehensive
Fifth-year |
Automobile Maintenance Level C
Tutorial
|
| 2 |
Car Maintenance Level
C Promotion Class
Car maintenance level
C coaching |
Automotive
component
disassembly
and assembly |
Automotive component
measuremen
|
|
Introduction to Automobile Engine Internship Factory |
| Laboratory introduction |
| In recent years, with the rise of computer technology, traditional old-fashioned cars
are facing elimination, and the era of comprehensive new technology has arrived. The
demand for talents in brain diagnosis, repair and signal analysis is very urgent,
especially as Taiwan is a country with a high density of automobiles. Brain-based
diagnosis technology involves basic principles such as basic electricity, electronics,
and introduction to electrical engineering, and the main function of this laboratory is
It is a course that uses computer diagnostic equipment and all the basic concepts
required for diagnosis of various instruments. Through the training of diagnostic
courses.The auto repair industry provides the talent needed for the future. This
laboratory is also a training venue for the Level C course of "Car Maintenance",
equipped with The new diagnostic equipment fully meets the requirements of
candidates. It helps students obtain the Class C automobile maintenance certificate
and helps them successfully pass the examination. Obtain the certificate. |
| Teaching objectives: |
| 1. |
Let students understand the skills and knowledge of the following internship
projects: such as identification of components such as starting, charging, lighting,
and signals in the automotive electrical system. |
| 2. |
Resistance measurement, circuit measurement and repair, component disassembly
and assembly, full vehicle maintenance, etc. |
| 3. |
Make students familiar with the functions, structures and disassembly and
assembly skills of each component. |
| 4. |
Cultivate students’ proper professional ethics and work attitude. |
|
| Equiments: |
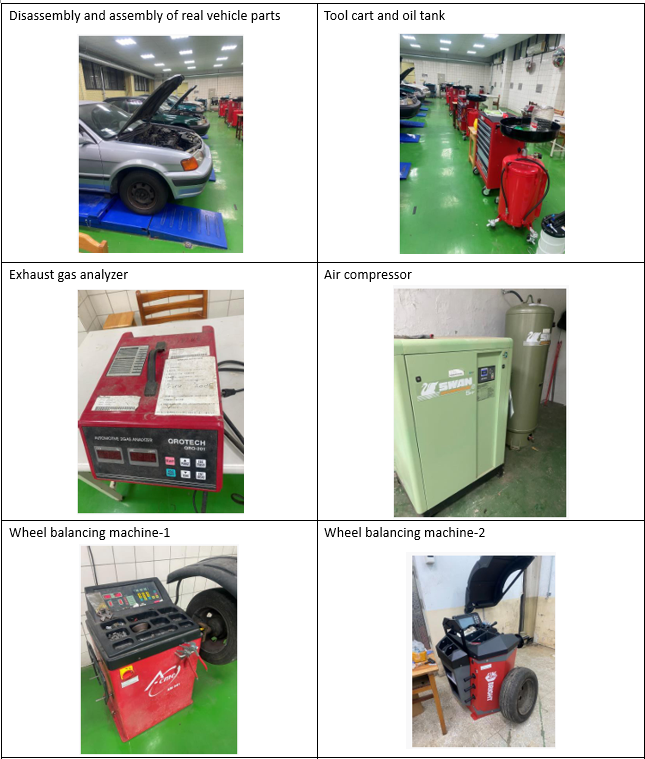 |
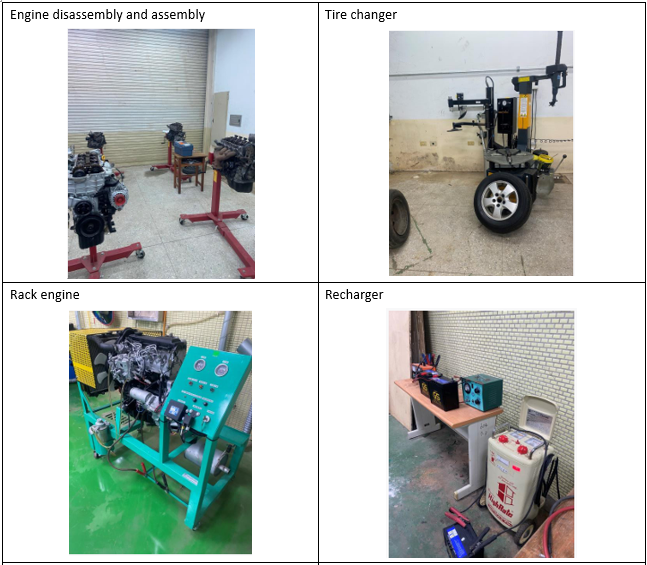 |